Chapter Events
Chapter Events are scripted sequences that trigger when a Player reaches a certain spot on the map.
Goals
Facilitate the creation of narrative scenes with reusable actions and a flexible structure.
How to create a Chapter Event
The first step to creating a Chapter Event is to create a ChapterEventPlayer and set how it will be triggered (Area, another Player, or Cave). For Area‑based triggers, also add a ChapterEventTrigger.
All levels contain a proposed structure for setting up Narrative nodes:
- Level
- Narrative
- Triggers: where
ChapterEventTriggers should be set - Paths: where
Path2Ds should be set - Players: where
ChapterEventPlayers should be set
- Triggers: where
- Narrative
ChapterEventPlayer
Add a new Node and choose ChapterEventPlayer.
Editor helper: when editing a ChapterEventPlayer, the inspector assists saving the ChapterEventData to its default path and adding it to the NarrativeManager database if needed.
Every child of ChapterEventPlayer must be a type of Event (extend BaseChapterEvent).
Data (ChapterEventData)
Set the data property to a ChapterEventData resource. It holds identity, conditions, and runtime config:
id: unique identifier used for saves. Valid formats includechapter_*/scene_*,chapter_*/arena_*,chapter_*/boss_*(e.g.,chapter_01/scene_02).can_repeat: if true, the event can trigger multiple times.has_seen_event/has_not_seen_event: gating conditions by other event ids.player_can_interact: if true, the Player can move/act during the event.use_cutscene_vignette: show cutscene vignette during the sequence.hide_hud: hide HUD during the sequence.
Triggering a Chapter Event
Set trigger_mode on the ChapterEventPlayer and wire trigger_path accordingly.
AREA
Instantiate res://src/Narrative/ChapterEvent/ChapterEventTrigger.tscn (base collision already configured). Add a CollisionShape2D as a child and size it to define the trigger area. Point trigger_path to this node.
PLAYER
Set trigger_path to another ChapterEventPlayer. This event plays automatically when the other player emits finished (avoid circular chains).
CAVE
Set trigger_path to a Cave. This event plays when the cave emits entered_cave.
NONE
No automatic trigger. Call play() via script or tests to start the sequence.
Adding Events
Events are added as nodes to the ChapterEventPlayer. You can see the full list of Events by opening the Create New Node dialog and searching for Event.
Every class that is a child of BaseChapterEvent can be used:
How it works
A ChapterEventPlayer is responsible for executing a sequence of events in order.
Depending on trigger_mode, it listens to an Area trigger (ChapterEventTrigger), another Player's finished, or a Cave's entered_cave to start playback.
When playing, ChapterEventPlayer iterates through its child nodes (each should extend BaseChapterEvent) and executes them.
If an event isn't finished, the system will wait for a finished signal from the event node before proceeding to the next.
Both ChapterEventPlayer and BaseChapterEvent have started and finished signals if you need to track their execution.
All event scripts must have a custom class name - so that they are exposed in the "Create New Node" dialog - and should start with Event....
Creating a Custom Event
To create a new event, extend BaseChapterEvent and implement your _play() method.
This method must return true or false, signaling if the event is completed.
Example of an instantaneous event:
class_name EventRemoveNode
extends BaseChapterEvent
export var node_path: NodePath
func _play() -> bool:
var node: Node = get_node(node_path)
node.get_parent().remove_child(node)
node.queue_free()
return true
If an event performs an action that takes time (e.g., animations), it must return false and call _finished() when complete.
Example of an asynchronous event:
class_name EventWaitForTimer
extends BaseChapterEvent
export var duration: float = 1.0
func _play() -> bool:
var timer := get_tree().create_timer(duration)
timer.connect("timeout", self, "_on_timer_timeout", [], CONNECT_ONESHOT)
return false
func _on_timer_timeout() -> void:
_finished()
Additional hooks and utilities:
on_sequence_started()/on_sequence_ended()are called at the start/end of the full sequence.- Implement
_force_finished()in asynchronous events to handle skipping in editor/debug (e.g., using the skip action); call_finished()at the end. - For debug builds,
debug_bypasson an event immediately marks it finished.
Basic flow of an event
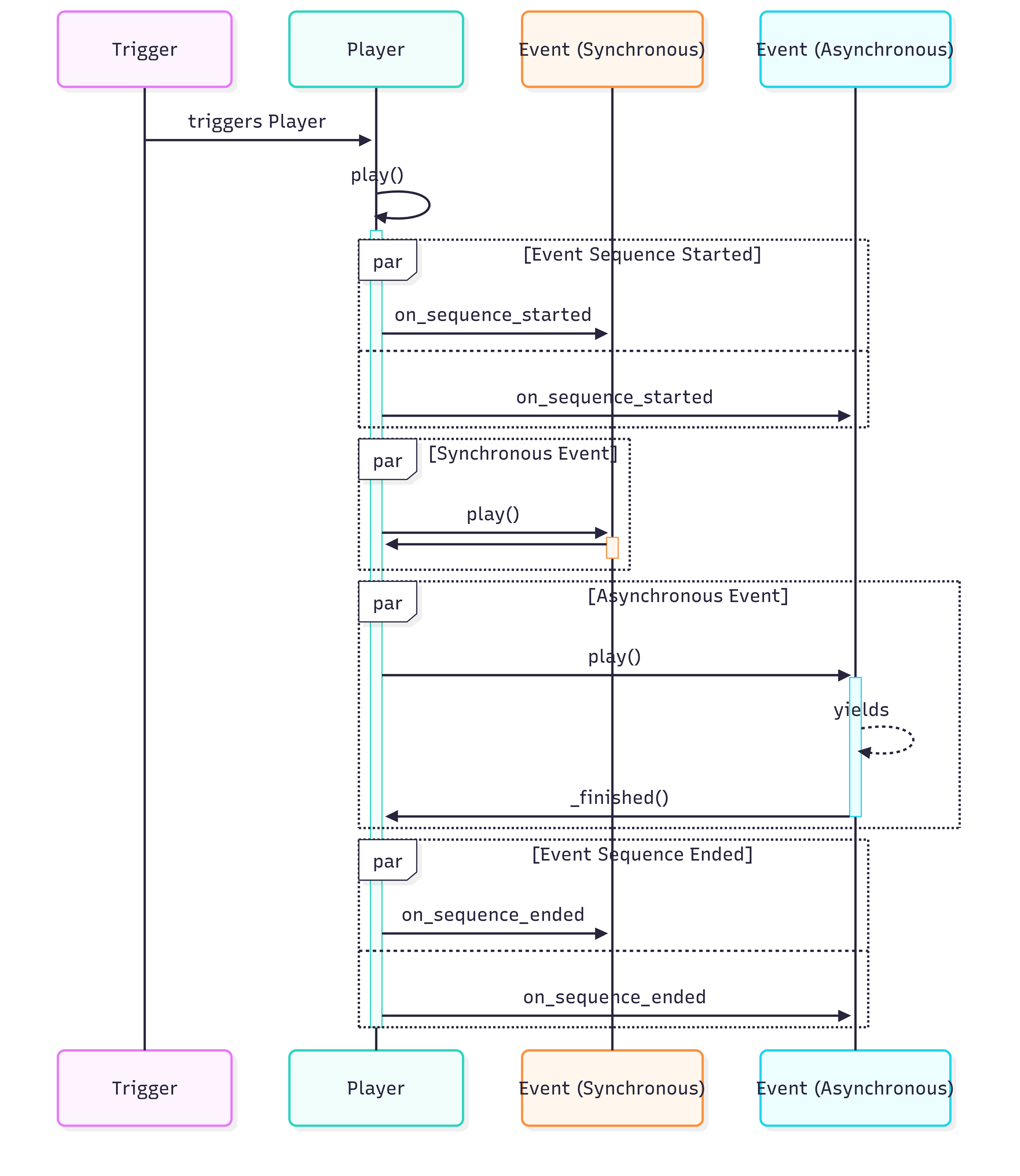
sequenceDiagram
participant T as Trigger
participant P as Player
participant ES as Event (Synchronous)
participant EAS as Event (Asynchronous)
T->>P: triggers Player
P->>P: play()
activate P
par Event Sequence Started
P->>ES: on_sequence_started
and
P->>EAS: on_sequence_started
end
par Synchronous Event
P->>ES: play()
activate ES
ES->>P:
deactivate ES
end
par Asynchronous Event
P->>EAS: play()
activate EAS
EAS-->>EAS: yields
EAS->>P: _finished()
deactivate EAS
end
par Event Sequence Ended
P->>ES: on_sequence_ended
and
P->>EAS: on_sequence_ended
end
deactivate P
With what script it communicates
Events can control: Player, GameplayCamera, NPCs, Enemies.
Events can trigger: Dialogue, Inner Monologue.
Saving: ChapterEvent data (start/end/last event) is stored via NarrativeManager. After a sequence finishes, the system requests saving the current slot.